The scientific giant Einstein once predicted that "the future development of science is nothing more than continuing to advance towards the macro and micro worlds.". Currently, nanotechnology, which is at the forefront of the micro world, has quietly brought various changes to human life. Further control of material molecules and atoms through nanotechnology will trigger a more profound technological revolution than micrometer technology. Nanotechnology has been widely applied in modern medicine and the field of life and health, and its role in improving the bioavailability of drug formulations and improving drug adherence is particularly prominent. For example, in recent years, nanotechnology has been applied to anti-aging substance NMN discovered based on aging molecular regulatory mechanisms, bringing significant effects.
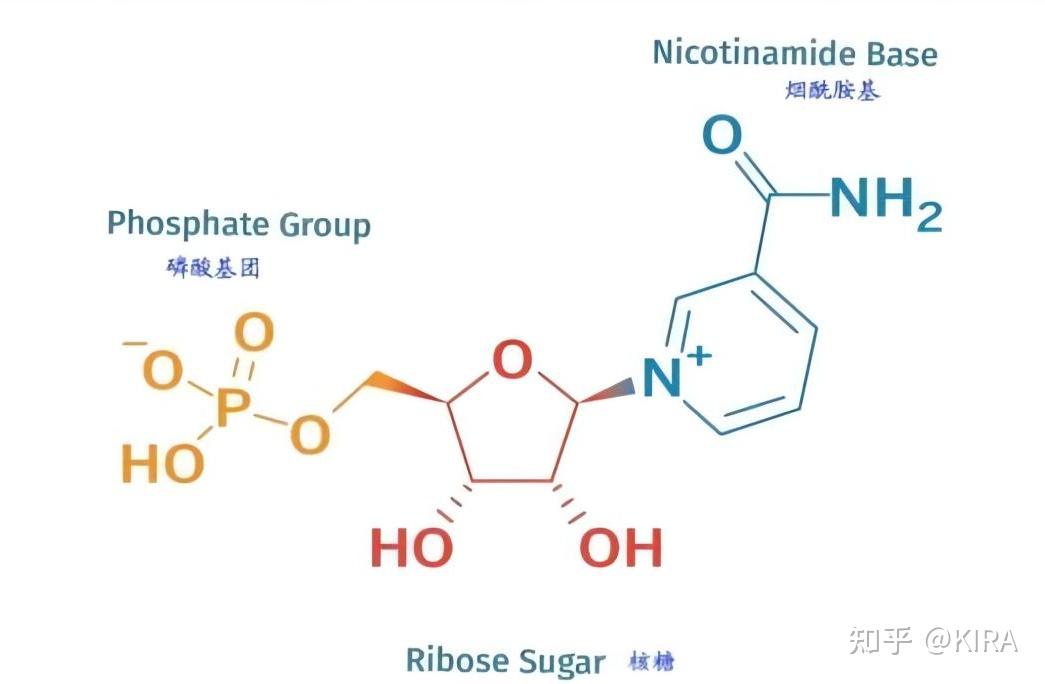
The molecular structure of NMN
NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide), also known as Nicotinamide Mononucleotide, is a naturally occurring bioactive nucleotide with a structure that can be divided into α and β Two isomers, among which only β- NMN is a naturally occurring form with biological activity.
In the human body, NMN is a precursor of NAD+(Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide, also known as CoI), and its function is mainly reflected through NAD+. NAD+exists in every cell of our body and plays an important role in various cellular metabolic reactions, mediating and participating in various biological processes. Over 300 enzymes rely on NAD+to function. However, as we age, NAD+in the human body decreases by about half every 20 years. The decrease in NAD+levels will lead to a decrease in DNA repair ability, and the accumulation of DNA damage will further drive the aging process to accelerate. The decline of NAD+during aging is also considered a major cause of diseases and disabilities, such as hearing and vision loss, cognitive and motor dysfunction, immune deficiency, arthritis caused by autoimmune inflammation, metabolic disorders, and cardiovascular diseases, all of which can be slowed down or even reversed by restoring NAD+levels.
NAD+participates in various human reactions
NAD+has a large molecular weight and is difficult to enter cells through the cell membrane, so it is generally achieved through the supplementation of NAD+precursor substances to achieve autonomous synthesis of NAD+. Research has found that other NAD+precursors such as tryptophan (Trp), niacin (NA), and nicotinamide ribose (NR) are structurally similar to NMN, all containing pyridine ring structures. However, there are some drawbacks and limitations in their practical applications. Therefore, NMN is still recognized globally as one of the most effective anti-aging substances and the best way to supplement NAD+.
After oral administration of NMN into the digestive tract, NMN is easily metabolized by CD38+into NAM (niacinamide) in the liver and loses its effectiveness. Nanotechnology will effectively improve this situation. Nicholas J. Hunt et al. from the University of Sydney, Australia, published a paper titled "Quantum Dot Nanomedicine Formula" in ACS NANO
The molecular structure of NMN
NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide), also known as Nicotinamide Mononucleotide, is a naturally occurring bioactive nucleotide with a structure that can be divided into α and β Two isomers, among which only β- NMN is a naturally occurring form with biological activity.
In the human body, NMN is a precursor of NAD+(Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide, also known as CoI), and its function is mainly reflected through NAD+. NAD+exists in every cell of our body and plays an important role in various cellular metabolic reactions, mediating and participating in various biological processes. Over 300 enzymes rely on NAD+to function. However, as we age, NAD+in the human body decreases by about half every 20 years. The decrease in NAD+levels will lead to a decrease in DNA repair ability, and the accumulation of DNA damage will further drive the aging process to accelerate. The decline of NAD+during aging is also considered a major cause of diseases and disabilities, such as hearing and vision loss, cognitive and motor dysfunction, immune deficiency, arthritis caused by autoimmune inflammation, metabolic disorders, and cardiovascular diseases, all of which can be slowed down or even reversed by restoring NAD+levels.

NAD+participates in various human reactions
NAD+has a large molecular weight and is difficult to enter cells through the cell membrane, so it is generally achieved through the supplementation of NAD+precursor substances to achieve autonomous synthesis of NAD+. Research has found that other NAD+precursors such as tryptophan (Trp), niacin (NA), and nicotinamide ribose (NR) are structurally similar to NMN, all containing pyridine ring structures. However, there are some drawbacks and limitations in their practical applications. Therefore, NMN is still recognized globally as one of the most effective anti-aging substances and the best way to supplement NAD+.
After oral administration of NMN into the digestive tract, NMN is easily metabolized by CD38+into NAM (niacinamide) in the liver and loses its effectiveness. Nanotechnology will effectively improve this situation. Nicholas J. Hunt et al. from the University of Sydney, Australia, published a paper titled "Quantum Dot Nanomedicine Formula" in ACS NANO


